In June 2021, providers of unified payments interfaces (UPI) in India recorded a total of 2.8 billion digital payment transactions worth over five trillion Indian rupees. This was an increase compared to May 2021, according to Statista research. It also underscores that in the financial year 2022, digital payments in India reached a total of over 239 billion Indian rupees. This marks a significant increase from 20.7 billion Indian rupees in the financial year 2018. The emergence of UPI or unified payments interface is an initiative by the Government of India to introduce a standardized protocol where banks, bank-like organizations, and non-bank entities could communicate with one another so as to make India’s payment system digital native.
What is UPI or Unified Payment Interface?
Launched in 2016, UPI is a National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) payment system that allows online payment and cashless money transfer using a simple mobile system.
UPI works on the concept of virtual payment addresses, which makes it interoperable- the greatest advantage that changed the payment landscape in India. UPI leverages the present infrastructure for authentication and enables one-click payment. By eliminating the need for sharing sensitive information like bank account numbers and One-time passwords (OTP), UPI has facilitated a safe, secure, and game-changing digital transition toward India’s nearly cashless economy. Unified Payment Interface is a platform that is both backward compatible as well as futuristic. Yet, when we speak of safety, there are a few things that are at stake.
What’s at stake during UPI Transaction?
A two-way payment transaction begins with a need for the sender or an entity that needs to transfer money to the receiver or second entity. Both entities could be either individuals or merchants or even government organizations. Three core requirements to be met for completing a payment transaction using UPI include sender authentication, receiver identification, and authorization. During these steps security at the infrastructure remains a major pain point of the UPI. Banks do not have a core competency of safely transmitting information, and placing the entire burden of two-factor authentication on the banking systems leads to insecure communication channels and non-standard authentication processes among different institutions.
So even while the reason for UPI’s success is a modern unique identifier for every individual, there are certain things that remain at stake, which are-
- Virtual payment addresses & Individual’s Digital identity
- UPI ecosystem that’s built and integrated for provisioning services
- Security of the identity, transaction information, and data over the network
- Response Time since the speed of transaction is the highest
Some of the other things also include regulatory compliance, financial and reputational aspects, and confidence of customer and market trust.
Ensuring UPI Security
Cyber security of Unified Payment Interface is targeted towards four main offerings which include process controls, functional controls, technology controls, and vulnerability detection. Across these four offerings, a product owner should consider the following points for UPI security-
- Ensure that the UPI environment and interfacing systems are secure
- Security of identity on mobile devices must be ensured
- An organization must introduce new security tools in context with the changing business model
- To ensure effective monitoring and analysis of security risks, advanced and smart analytics tools must be used
- Compliance with regulations and adopting industry standards help in further strengthening the security of UPI
OWASP Mobile Top 10 2022 for UPI Security
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a non-profit foundation which provides remediation guidance to improve software security. OWASP Mobile Top 10 provides a ranking and most critical security risks for mobile application, alongside suggestions on how to remain protected against these attack vectors. The top 10 attack vulnerabilities OWASP Mobile Top 10 in 2022 are-
- M1: Improper Platform Usage
- M2: Insecure Data Storage
- M3: Insecure Communication
- M4: Insecure Authentication
- M5: Insufficient Cryptography
- M6: Insecure Authorization
- M7: Client Code Quality
- M8: Code Tampering
- M9: Reverse Engineering
- M10: Extraneous Functionality
Security Considerations: 5-Step Roadmap to Create Secure UPI Product
The proportion of UPI transactions in the total volume of digital transactions grew from 23% in 2018-19 to 55% in 2020-21 with an average value of ₹1,849 per transaction. The volume of UPI transactions calls for security considerations in place to create a secure UPI product that ensures customer trust and retention. Valuebound recommends following UPI security considerations to ensure benefit-realization of the product (Fig. 1).
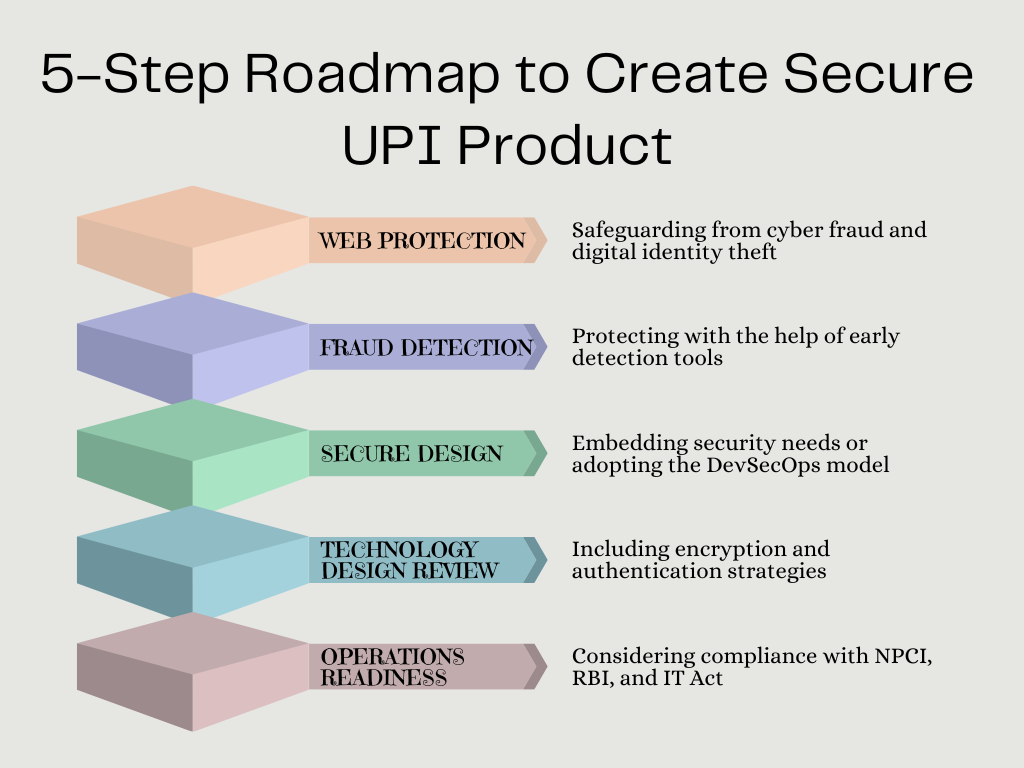
Web Protection
This includes protection from cyber fraud and safeguarding digital identity. Google Pay, for instance, suggests prerequisites for integrating it with a site. These include-
- Ensuring that business channels are verified merchants by NBFC/ banks
- Ensuring that all details needed to accept payment using UPI ID are available
- Ensuring to have required APIs from the bank to check payment status
- Ensuring that every transaction uses a unique transaction ID
Fraud Detection
Early detection tools can reduce Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) for new-age frauds like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), ransomware, application vulnerability exploits, merchant frauds, spam, reconnaissance attacks, software supply chain attacks, and account takeovers.
Secure Design
Embedding security needs or adopting the DevSecOps model in the development programme helps in putting cybersecurity at the central part of the production pipeline.
Technology Design Review
Encryption and authentication strategies like public key infrastructure (PKI) and hardware security modules (HSM) help secure UPI product. Network architecture, application program interface (API) and interface security form an integral part of technology design review.
Operations Readiness
A new UPI product should have compliance with National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), Reserve Bank of India, and IT Act guidelines to avoid compliance and regulatory hiccups. UPI security also includes log maintenance and advanced log analytics.
Conclusion
In 2021, out of the 2.8 billion transactions, PhonePe had a share of 46 percent and GooglePay a share of 35 percent. Third big player is Paytm with a share of nearly 12 percent. The volume of UPI transactions and India’s digital ecosystem is a testimony that the scaled-up mobile banking infrastructure is here to stay and transform the economy. Creating a secure UPI ecosystem becomes more important due to the exponentially growing customer base. If you wish to learn how Valuebound processes solutions to ensure a safe and secure UPI product for you, get in touch with us.