In a survey of 750 global cloud decision-makers and users, conducted by Flexera in its 2020 State of the Cloud Report, 83% of enterprises indicate that security is a challenge, followed by 82% for managing cloud spend and 79% for governance.
For cloud beginners, lack of resources/expertise is the top challenge; for advanced cloud users, managing cloud spend is the top challenge. Respondents estimate that 30% of cloud spend is wasted, while organizations are over budget for cloud spend by an average of 23%.
56% of organizations report that understanding cost implications of software licenses is a challenge for software in the cloud.
This highlights the importance of careful planning and management when migrating to the cloud.
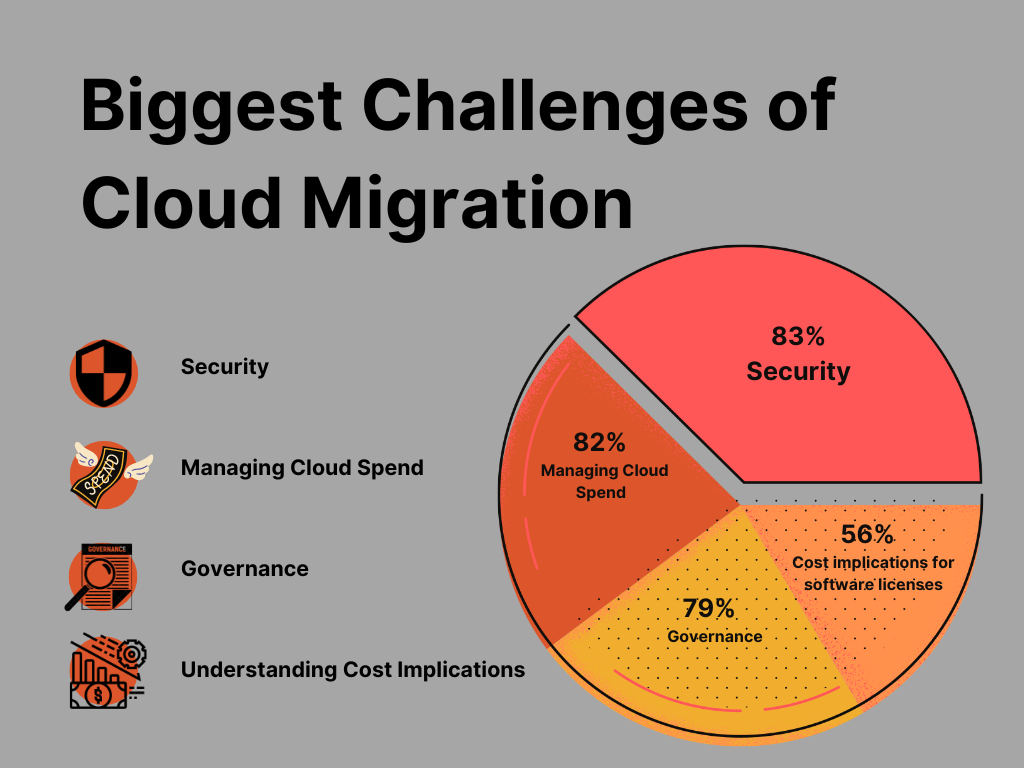
Addressing the Pain Points of Cloud Migration for Businesses
The migration process presents several pain points that businesses need to consider and address. Apart from the aforementioned challenges, here are some common pain points that businesses may encounter during a cloud migration:
- Legacy Systems and Infrastructure: Many businesses have existing legacy systems and infrastructure that may not be compatible with cloud technologies. Migrating from these systems can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and consideration.
- Data Security and Privacy: Moving data to the cloud introduces new security risks and requires robust security measures to protect sensitive information. Businesses need to carefully evaluate their cloud service provider's security practices and consider compliance requirements.
- Downtime and Disruptions: During the migration process, businesses may experience temporary service interruptions and downtime. This can impact productivity and customer experience, so having a detailed migration plan that minimizes disruptions and includes appropriate backup and disaster recovery strategies is crucial.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating cloud services with existing on-premises systems and applications can be challenging. Compatibility issues, data synchronization, and API integration complexities may arise, requiring thorough testing and development effort.
- Vendor Lock-in: Businesses need to be mindful of potential vendor lock-in when choosing a cloud service provider. Switching providers or moving data back to on-premises infrastructure can be difficult and costly. Careful evaluation of vendor contracts and ensuring data portability can mitigate this risk.
- Cost Management: While cloud migration can lead to cost savings in the long run, it is essential to manage costs effectively. Unexpected expenses, such as data transfer fees, storage, and licensing fees, must be considered and monitored to avoid budget overruns.
- Employee Training and Skill Gaps: Cloud technologies often require new skill sets and knowledge for managing and optimizing cloud infrastructure. Providing adequate employee training and upskilling opportunities can help address skill gaps and ensure smooth operations in the cloud environment.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Different industries and regions have specific compliance and regulatory requirements regarding data storage, privacy, and security. Businesses must ensure that their cloud migration strategy aligns with these requirements to avoid legal and compliance issues.
- Performance and Scalability: While the cloud offers scalability, businesses need to design and configure their cloud infrastructure properly to handle increased workloads and maintain optimal performance. Poorly planned cloud architectures may lead to performance issues or unexpected costs.
- Change Management and Cultural Shift: Migrating to the cloud often involves a significant cultural shift within the organization. Employees may resist change or face challenges in adapting to new workflows and processes. Effective change management strategies, communication, and training can help address these issues.
It's important for businesses to carefully plan and address these pain points during the cloud migration process. By doing so, they can mitigate risks, ensure a smoother transition, and fully leverage the benefits of cloud computing.
How cloud migration can benefit businesses?
Key benefits have been observed by organizations that have migrated to the cloud. Here are a few reasons:
- Cost Savings: Cloud computing achieves cost savings through the pay-as-you-go model. Instead of investing in expensive on-premises servers, businesses utilize cloud services, paying only for the resources they consume. This eliminates upfront hardware costs, reduces maintenance expenses, and optimizes resource allocation, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud platforms provide businesses with the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. This scalability is achieved by leveraging the cloud provider's infrastructure, which can quickly allocate additional computing power, storage, or network resources as needed. Businesses can adjust their resource allocation in real-time, accommodating fluctuations in traffic or workload without the need for significant hardware investments.
- Collaboration and Productivity: Cloud-based collaboration tools enable seamless teamwork and enhanced productivity. Real-time document sharing allows multiple users to work on the same file simultaneously, improving collaboration and reducing version control issues. Virtual meetings and instant messaging enable efficient communication and collaboration regardless of physical locations, promoting remote work and flexibility.
- Disaster Recovery and Data Resilience: Cloud providers offer robust backup and recovery solutions to ensure data protection and quick restoration. Redundant data storage across multiple locations and geographically distributed servers minimize the risk of data loss. Automated backup mechanisms regularly create copies of data, reducing the recovery time objective (RTO) in the event of an outage or disaster.
- Improved Security Measures: Cloud service providers prioritize security and employ dedicated teams to monitor and address security threats. Advanced security technologies, such as data encryption, help protect sensitive information. Identity and access management tools ensure authorized access to data and applications. Compliance certifications validate that the cloud provider meets industry-specific security standards and regulations.
- Access to Advanced Technologies: Cloud providers invest in and offer a wide array of advanced technologies and services. Businesses can leverage these technologies without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware or software infrastructure. For example, businesses can utilize cloud-based machine learning services to analyze large datasets, extract insights, and make data-driven decisions. This access to advanced technologies empowers businesses to stay competitive, innovate, and enhance customer experiences.
By harnessing the capabilities of cloud computing, businesses can leverage these "how" factors to drive efficiency, agility, collaboration, and security, ultimately enhancing their overall operations and performance.
Use Cases with Proven Results of Cloud Migration
Here are some examples and use cases that highlight the proven results of each of the cloud benefits.
Cost Savings
Airbnb: By migrating to the cloud, Airbnb reduced costs by an estimated $15 million per year. They no longer needed to maintain and manage their own data centers, resulting in significant cost savings.
Scalability and Flexibility
Netflix: Netflix utilizes the scalability of the cloud to handle massive spikes in user demand. During peak usage times, they can quickly scale their infrastructure to deliver seamless streaming experiences to millions of viewers worldwide.
Collaboration and Productivity
Slack: The cloud-based collaboration platform, Slack, has transformed how teams work together. It provides real-time messaging, file sharing, and collaboration features, enabling teams to communicate and collaborate efficiently, irrespective of their physical locations.
Disaster Recovery and Data Resilience
Dow Jones: Dow Jones, a global media and publishing company, leverages the cloud for disaster recovery. By replicating their critical data and applications to the cloud, they ensure business continuity in the event of an outage or disaster, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Improved Security Measures
Capital One: Capital One, a leading financial institution, migrated their infrastructure to the cloud and implemented advanced security measures. They utilize encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring to enhance the security of their customer data, providing a secure banking experience.
Access to Advanced Technologies
General Electric (GE): GE utilizes cloud-based analytics and machine learning to optimize their operations. By analyzing data from industrial equipment, they can identify patterns, predict maintenance needs, and improve efficiency, resulting in cost savings and increased productivity.
These examples demonstrate how organizations across different industries have successfully leveraged cloud computing to achieve specific benefits. While the results may vary for each business, these real-world use cases showcase the potential of cloud migration in driving positive outcomes.
General Steps and Best Practices for Cloud Migration
When it comes to migrating to the cloud, there are several steps and industry best practices that can help ensure a successful transition. While specific approaches may vary depending on the organization and their unique requirements, cloud service providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure often provide guidance and best practices to facilitate the migration process. The illustration below shows some general steps and best practices:
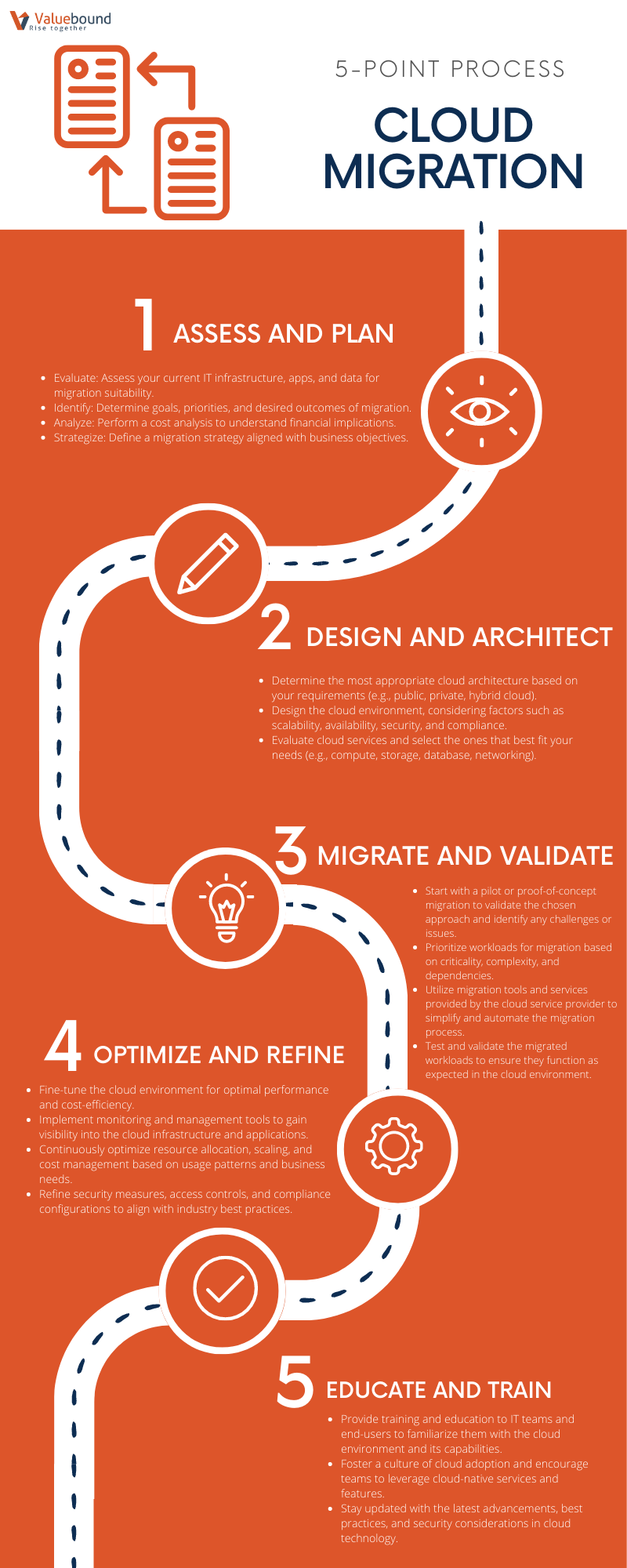
AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF) for migrating to the cloud
AWS (Amazon Web Services) offers a comprehensive set of resources, tools, and best practices to assist organizations in migrating to the cloud. They provide a step-by-step framework known as the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF) that helps businesses plan, prioritize, and execute their cloud migration strategy. Here are some key suggestions and best practices from AWS:
Establish a Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE)
- AWS recommends creating a dedicated team or CCoE responsible for driving the cloud migration initiative and ensuring alignment with business goals.
- The CCoE facilitates communication, provides governance, defines best practices, and shares knowledge across the organization.
Define the Business Case and Migration Strategy
- AWS suggests identifying the business drivers for cloud migration, such as cost savings, scalability, or agility, and translating them into specific goals.
- Determine the appropriate migration approach (e.g., lift-and-shift, re-platform, or refactor) based on workload characteristics and business requirements.
Assess the IT Environment
- Conduct a thorough assessment of existing applications, infrastructure, and data to understand dependencies, constraints, and readiness for migration.
- Utilize AWS tools like AWS Application Discovery Service and AWS Migration Hub to gather insights and inventory of on-premises resources.
Design the Cloud Architecture
- Follow AWS Well-Architected Framework principles to design a secure, scalable, and efficient cloud architecture.
- Leverage AWS services like Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, AWS Lambda, and others to build the desired cloud environment.
Plan and Execute the Migration
- Develop a detailed migration plan that includes timelines, resource allocation, and risk mitigation strategies.
- Use AWS services like AWS Server Migration Service (SMS) or AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) to simplify and automate the migration process.
- Validate and test the migrated workloads in the cloud to ensure functionality, performance, and security.
Optimize and Govern the Cloud Environment
- Continuously monitor, optimize, and refine the cloud environment to maximize performance and cost efficiency.
- Implement security measures following AWS Security Best Practices, including proper access controls, encryption, and monitoring tools.
- Establish governance mechanisms to enforce policies, track usage, and ensure compliance with organizational standards.
Unlock the Potential of the Cloud: Migrate Seamlessly with Valuebound
Migrating to the cloud offers numerous benefits for businesses, including cost savings, scalability, enhanced collaboration, improved security, and access to advanced technologies. By following industry best practices and leveraging the guidance provided by cloud service providers like AWS, organizations can navigate the migration process successfully.
As an AWS partner, Valuebound is well-equipped to assist businesses in their cloud migration journey. With our expertise and experience, we can provide the necessary support and guidance to plan, execute, and optimize cloud migrations. Whether it's assessing the IT environment, designing the cloud architecture, or ensuring governance and security, Valuebound can be your trusted partner throughout the entire migration process.
Don't miss out on the opportunities and advantages of cloud computing. Contact Valuebound today to explore how we can help your business embrace the power of the cloud. Take the first step towards a more agile, cost-effective, and innovative future.





