Accenture says, “Those that treat Open Banking as a strategic growth priority will position themselves to deliver the seamless and engaging digital experiences customers want—and potentially boost revenues by upwards of 10 percent.”
A reasonably mature FinTech environment with existing use cases of API-led banking has emerged in recent years. This has led to the development of a conducive environment for financial services companies, banks, and incumbent financial organizations- collectively called the financial institutions or FIs- to consider how they can mature in the quest to embark on their API-based open banking journey.
In our previous two parts of the open banking series, we explained why banks should adopt API-based open banking and the challenges and opportunities in adopting the same. We also demonstrated it through the successful use cases of top banks like HSBC and ICICI.
Our collection of three-part series of experience-driven insights on successful API integration for open banking models can help C-suite executives of FIs and banks navigate their way into a thriving digital future.
APIs, as we clearly see, have grown beyond their initial definitions of just letting two systems interact with one another. Today APIs have evolved as a full-fledged suite of services that all leadership personnel must understand in depth to adopt open banking.
So, what should be your internal capabilities? What are the key tenets for implementing an open banking ecosystem? Through our blog, we discuss them and develop a market-ready strategy for implementing an API-based open banking business model.
Internal Capabilities to Gauge Before Implementing Strategy for Open Banking
Before formulating a strategy for an API-based open banking business model, executives must gauge internal capabilities first. A gap analysis is necessary to identify loopholes and internal areas for building capabilities. Key stakeholders must assess the following four considerations (Fig. 1).
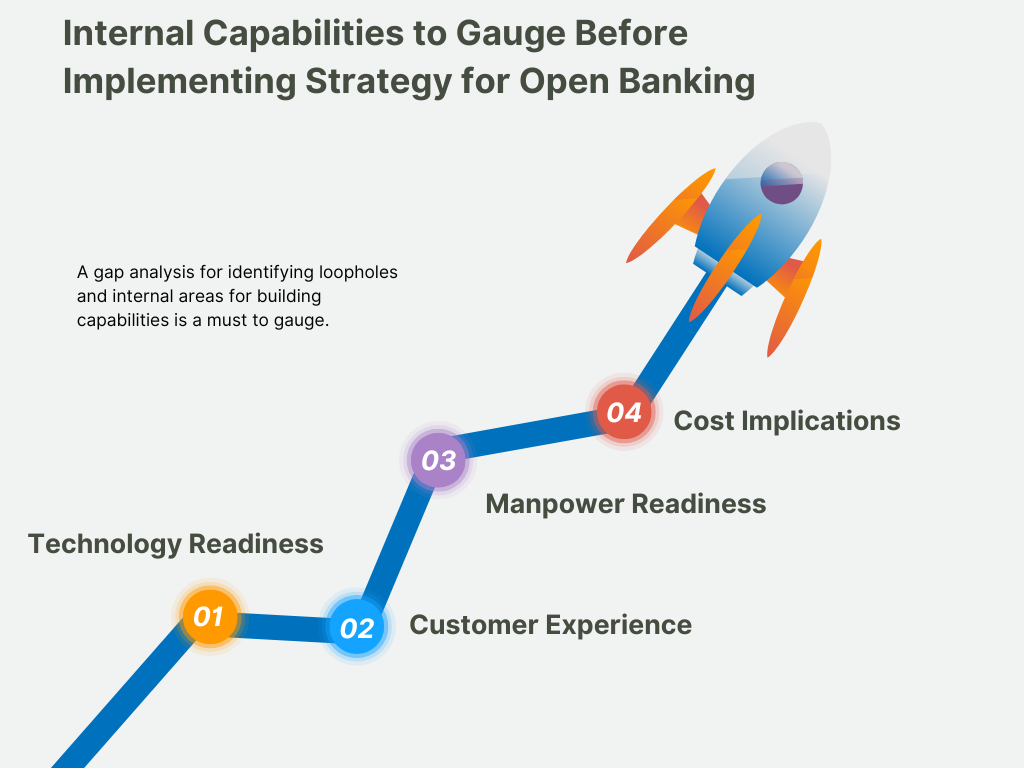
- Technology Readiness- Assess the current IT infrastructure of the FI and the ease of API integrations.
- Customer Experience- Understand customer needs and align them with product or service offerings.
- Workforce Readiness- Gauge whether an organization has manpower capabilities to integrate APIs or not.
- Cost Implications- Estimate the cost of API integration and technology upgrade.
Fundamental Tenets of Successful Open Banking Implementation
Five considerations serve as critical tenets for successfully implementing API-based open banking ecosystem. These include data sharing, data privacy and cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, partnerships or interoperability, and customer experience (Fig. 2).
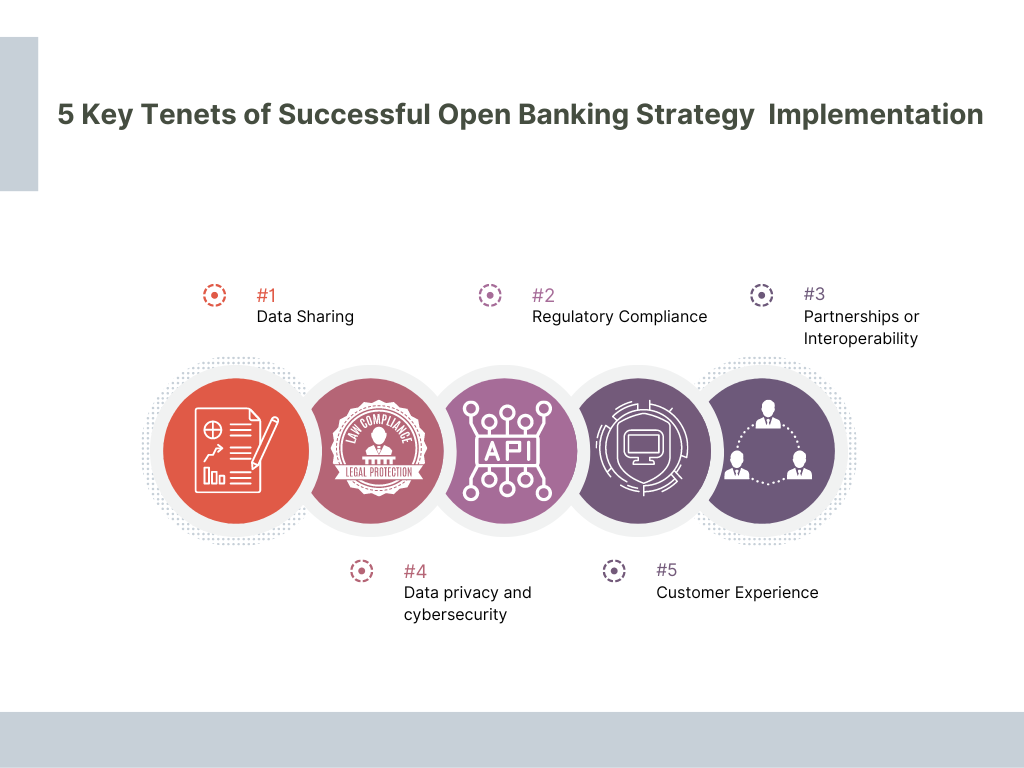
Data Sharing- Open banking is highly reliant on data sharing. It makes it possible for the customers to control the portability of critical financial data, which is shared with third parties for the ultimate benefit of customers. In addition, financial service companies can monetize customer data, given that open banking envisages secure data sharing. This can create another source of revenue for incumbent banks.
Data Privacy & Cybersecurity- Customer trust, market reputation and confidence, and service adoption- all lie at the heart of data protection. Compromising cybersecurity could be a costly mistake. C-suite executives can read our insights on the cybersecurity roadmap to gauge the risks and inculcate cybersecurity best practices. Hence, banks and financial services companies must ensure appropriate internal audits for data transfers to move toward open banking.
Regulatory Compliance- While developing and implementing an open banking ecosystem, there has been a differentiated approach of regulatory authorities across different jurisdictions. As a result, FIs must ensure compliance with data sharing, cybersecurity regulations, data privacy, consumer protection, and personal data protection.
Partnerships or Interoperability- Since API forms the premise of open banking, including banks and NBFCs, developing capabilities to strategize data, products, and services is critical. Following set standards in context with the security, customer experience, API, and operations eases the process of creating partnerships and interoperability.
Customer Experience- Open banking not only helps create additional revenue streams but also provides greater control for improved customer experience. This is possible through actionable insights based on data. Hence, creating customer-centric products and services becomes easier while reinstating customers’ trust in the brand.
Market-Ready Strategy for Open Banking
The average compounded annual revenue growth of banks and competing players in the Accenture study that utilize different business models (between 2018 and 2020) is
- 76% of digital-only players with non-linear models
- 44% digital-only players emulating traditional vertically integrated models
- <2% traditional banks with vertically integrated models
The revenue performance of digital-only, non-linear challengers is an inspiration for incumbent financial services companies, and banks for higher market valuations. So now the million-dollar question is how to facilitate a smooth “go-to-market”? Deloitte suggests three key areas that form essence of successful deployment of market strategy for API-based open banking (Fig. 3).

Developing Core Capabilities
As banks and financial services companies move towards developing core capabilities, their aim should be to develop an agile architecture that supports use cases for API enablement. Additionally, FIs must have organizational maturity for a seamless API management system, which includes API gateway, sandbox environment, and API lifecycle management.
To ensure optimum channel penetration and customer acquisition, banks and non-banks must have-
- Well-defined legal framework for liability and dispute management
- Capability building for personnel operating the system and acquiring the requisite skill set for APIs development
- Scalable, agile infrastructure to offer greater modularity and easier configuration
- Global FAPI (Financial grade API) and ISO 20022 standards to ensure adequate security controls
- Identification of verticals where API-enabled products and services can add value
Identifying and Prioritizing Relevant Use Cases
Financial institutions can leverage data to generate leads, cross-sell products, pre-, and post-delinquency management, risk assessment, and product development. Direct benefits of leveraging data for open banking are business augmentation, operational efficiency, improvement in asset quality, and cost optimization. For reaping all these benefits, banks and financial services companies must identify and prioritize the use cases to understand the relevance for their customers and the banks. Measure the intent to use, perceived benefits, and current experience for monetization, potential opportunity, and risk management.
Deloitte identifies the top 10 relevant use cases that form the basis of a successful market strategy for open banking. These are-
- Wealth Management – High relevance to FI
- Recurring payments – High relevance to customer
- Sweeping accounts and micro-saving accounts – Medium relevance to FI
- Credit risk assessment - High relevance to FI
- NPA management and collections - High relevance to FI
- Financial product aggregator - High relevance to customer
- Spend management - High relevance to customer
- Non-financial product aggregator – Low relevance to both banks, and customers
- Automated overdraft credit - High relevance to FI
- Automated payables reconciliation - High relevance to FI
Determining the Right Monetization and Pricing Strategy
The years to follow are promising for open banking, which is why banks have already started their journey toward API monetization. Banks can use robust pricing strategies for their competitive advantage by leveraging monetization opportunities and unlocking the full suite of API-enabled offerings.
Both free and premium APIs come with their own sets of monetization opportunities. Free-charge APIs facilitate services through third parties, which can help banks orchestrate unique customer experiences, intensify service penetration, and increase customer acquisition. Meanwhile, premium APIs monetization opportunities arise because banks can charge third parties for using them. Some of the pricing models for premium APIs can be
- Pay-per-use- No minimum fee, charge per call/per month
- Free + Premium- Free for basic; more information requires premium pricing
- Tiered- Tiered pricing for pre-defined buckets
- Fixed fee- A fixed or percentage of the transaction paid to the API provider
In Brief
While the global open banking wave is relatively low tide right now, there is a change building at the bottom of the seabed. Accenture says that $416 billion in revenue will be at stake as the open data wave arrives, and banks must decide between surfing on the wave or riding it out with minimal damage. The leaders of open banking tomorrow shall be the ones who prioritize APIs, agile partnerships, data custodianship, analytics mastery, and trusted security.
Valuebound helps banks and financial services companies win in the digital ecosystem and get ready for what’s next. Talk to us to know how you can create a successful go-to-market strategy for API-based open banking.



